Transmit Beamforming in 802.11ac requires explicit feedback from the beamformee on the current channel state, returned to the beamformer and used to weight the signals to each antenna.
Explicit Transmit Beamforming is introduced as part of 802.11ac which is introduced in Aruba with AOS 6.3 and AP 224/ 225.
Environment : Transmit Beamforming requires that both AP and client support the feature for it to work.
Mobility Controller (AOS 6.3) ------ AP 225s )) (( Clients (802.11ac capable) that support Explicit Transmit Beamforming as Beamformee.
Explicit Transmit beamforming is enabled by default. This is a per ssid configuration and can be done in "ht-ssid-profile".
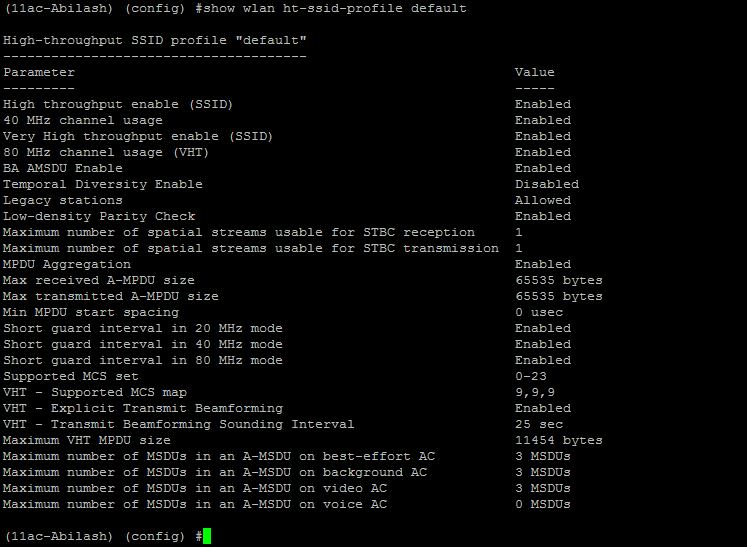
This can be disabled by turning off this knob - "VHT Explicit Transmit Beamforming".
When this is enabled, the evaluation of TxBF capable clients is done every 25msec. This value also be changed.
In case of 802.11n both Implicit and explicit beamforming were introduced, but were not clearly defined. Hence it was not widely used.
With 802.11ac, Implicit Beamforming has been discarded in favour of Explicit beamforming and is not well defined.
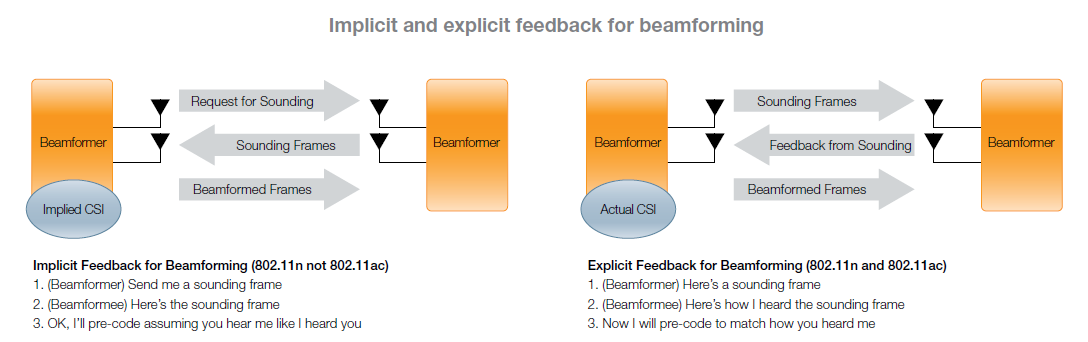
Below is the sequence of events that take place as part of Transmit Beamforming to get reports from clients.
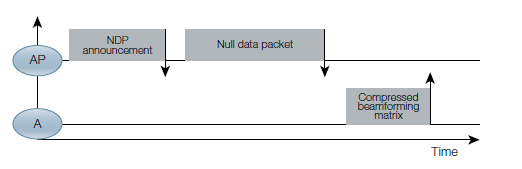
- AP sends an announcement that its going to send out a sounding frame containing data to be evaluated by client.
- AP sends the data in the Null data packet.
- All the clients supporting TxBF receive it as start responding to the report request by sending back a Compressed V-Matrix to the AP.
- Based on the feedback received by the AP from clients, it re-calibrates the phase shift for each of the transmitted signal from each antenna so that the signal strength reaches its maxima at client.