Beginners Guide to Spectrum Analysis
Using Chanalyzer with Wi-Spy DBx and Aruba AP225 converted to a spectrum monitor.
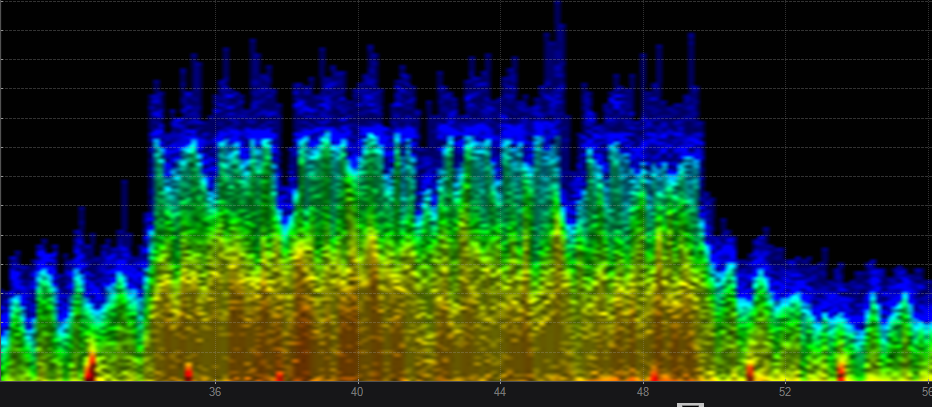
Spectrum analysis is a very handy tool to use when you encounter problems that happen to be RF related. Using a spectrum monitor can help you track down the cause of the problem. Below is just some examples of RF signatures you will likely encounter.
Chanalyzer is a very easy program to use. Just plug in your Wi-Spy and launch the program, and you will be scanning the 2.4 Ghz band.
With the Aruba set up you will need to create an AP group
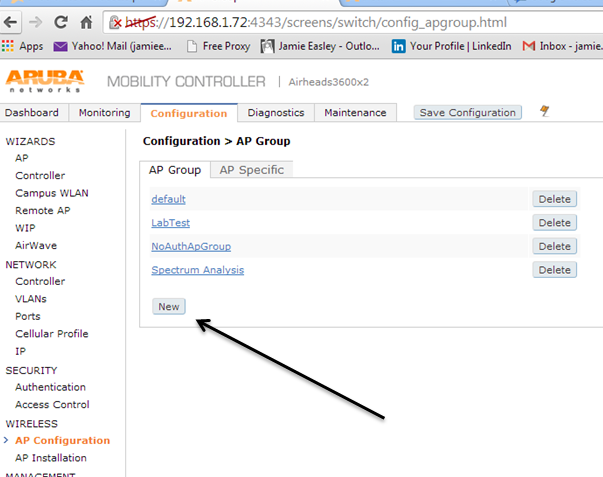
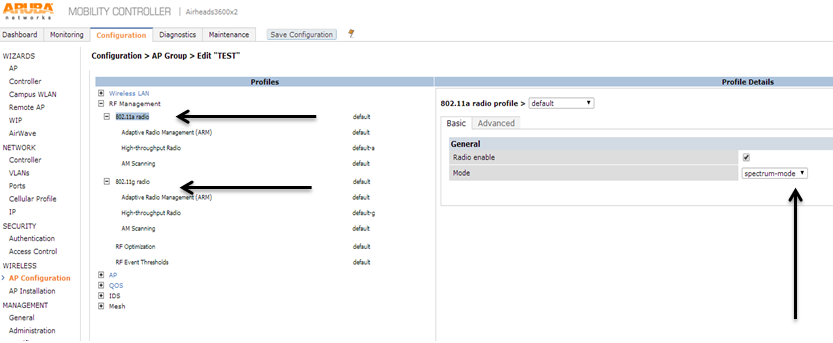
Now to add the config for the spectrum monitor. Click on the newly created AP group. Now click RF management. You will need to change both the A and G radio. Click the radio and change the mode to spectrum.
Now you need to provision an AP to that group. Check the box by the AP you want to provision.
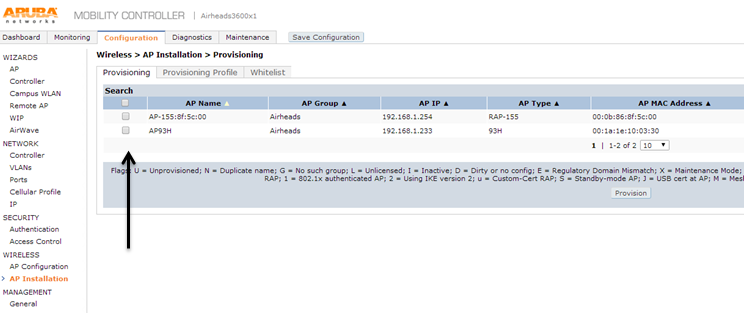
Then you will select the group you created.
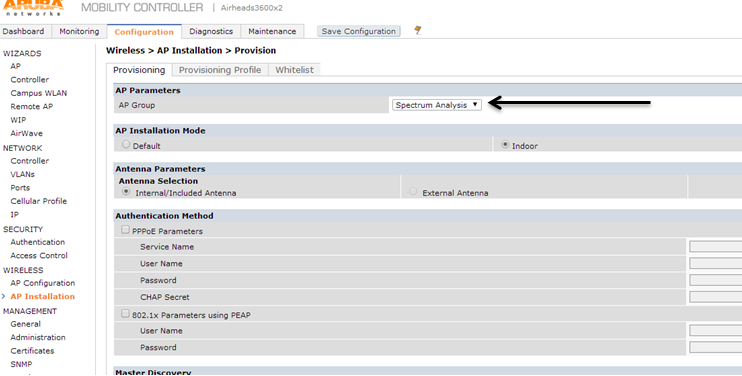
Scroll to the bottom and hit apply and reboot. When the AP comes back up it will be a spectrum monitor.
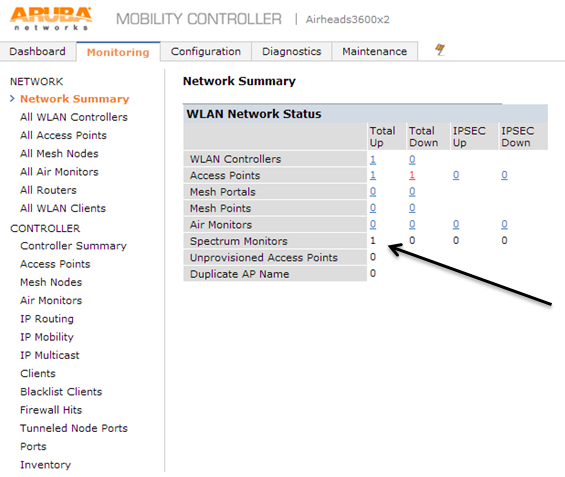
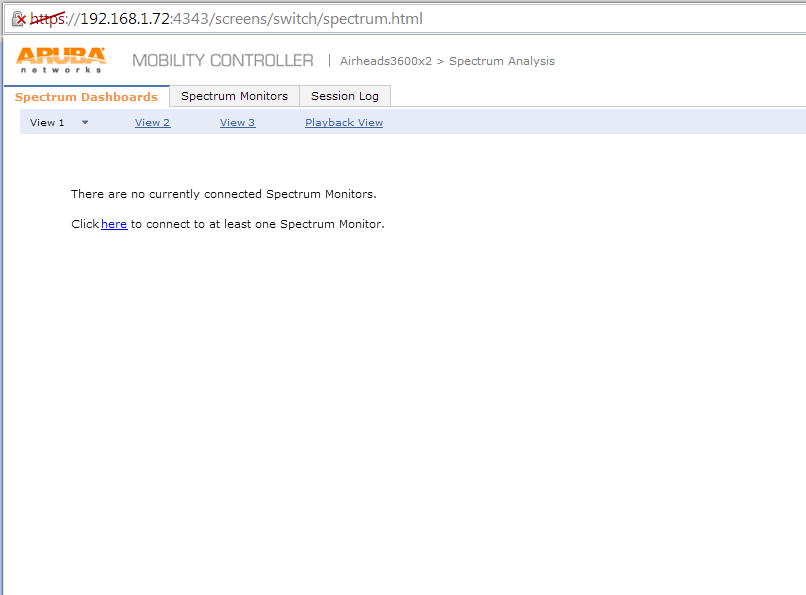
Now on the monitoring page click on Spectrum Monitors. It will launch an external page that requires Flash. You will need to add a monitor on this page.
It gives you the choice of APs provisioned as spectrum monitors. To connect click the MAC address and click connect.
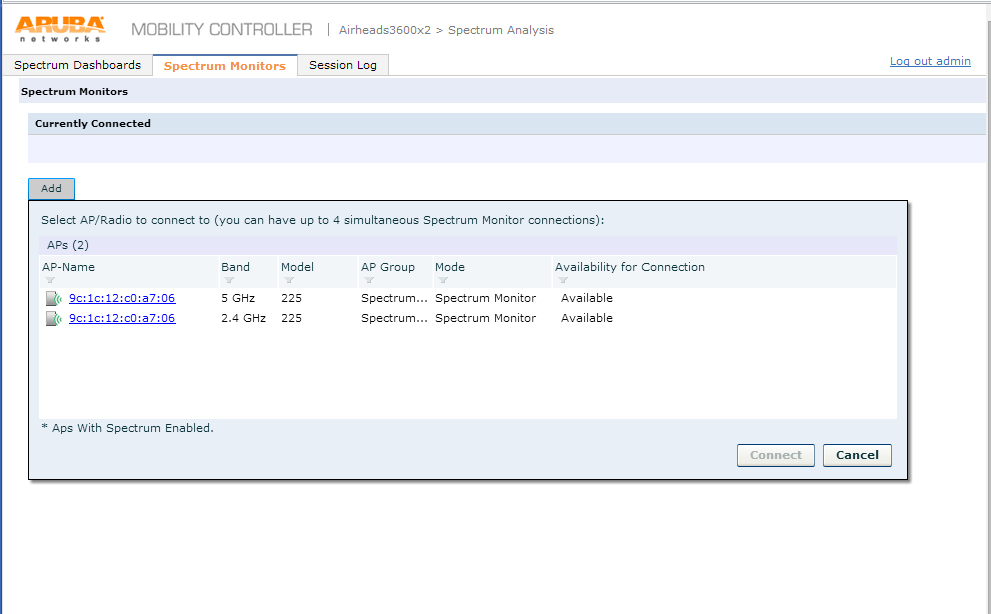
Then click the Mac address one more time to start using the spectrum monitor.
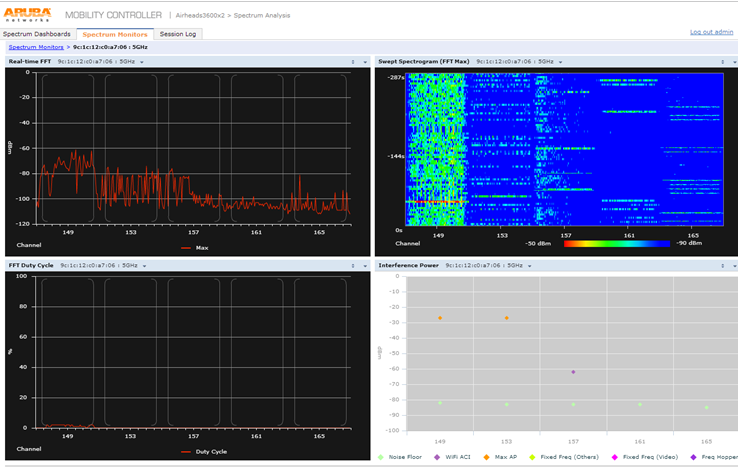
Now you are monitoring the spectrum with an Aruba AP.
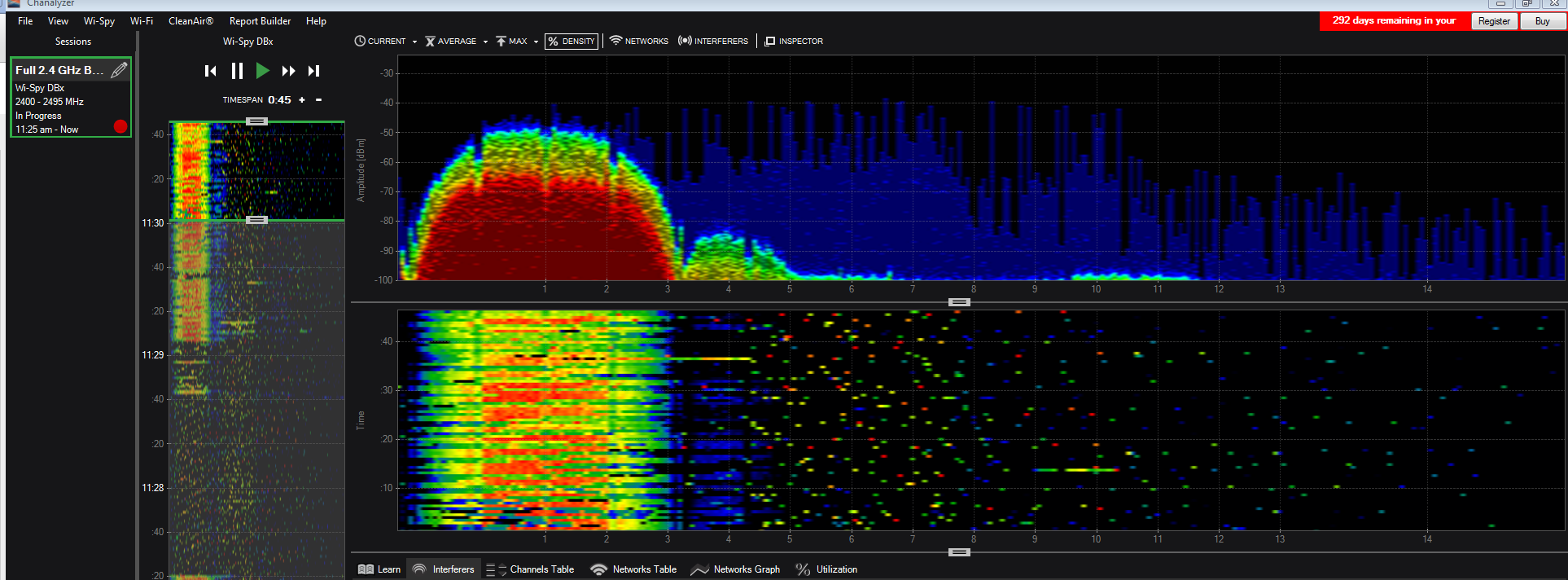
Here are a few RF signatures you will likely see in the field.
5.0 802.11 a

2.4 802.11b
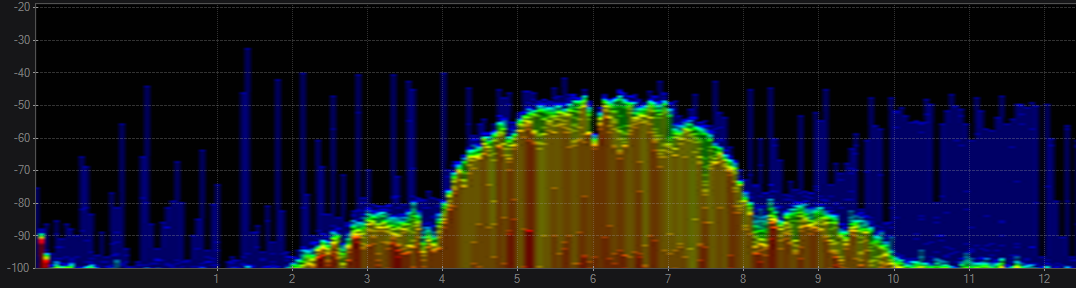
2.4 802.11 g
2.4 802.11 n 20Mhz
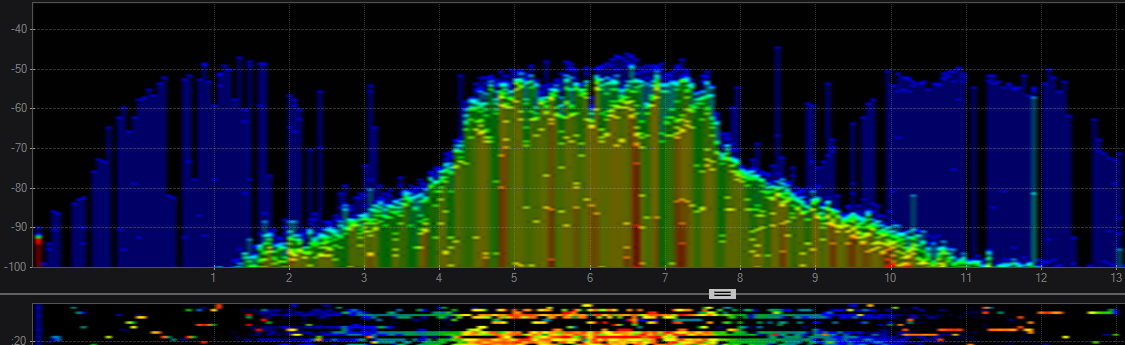
2.4 802.11 n 40 Mhz > This is why 40 Mhz channels aren’t recommended because the overlap of channels is severe. As you can see this has rendered 1 through 7 useless.
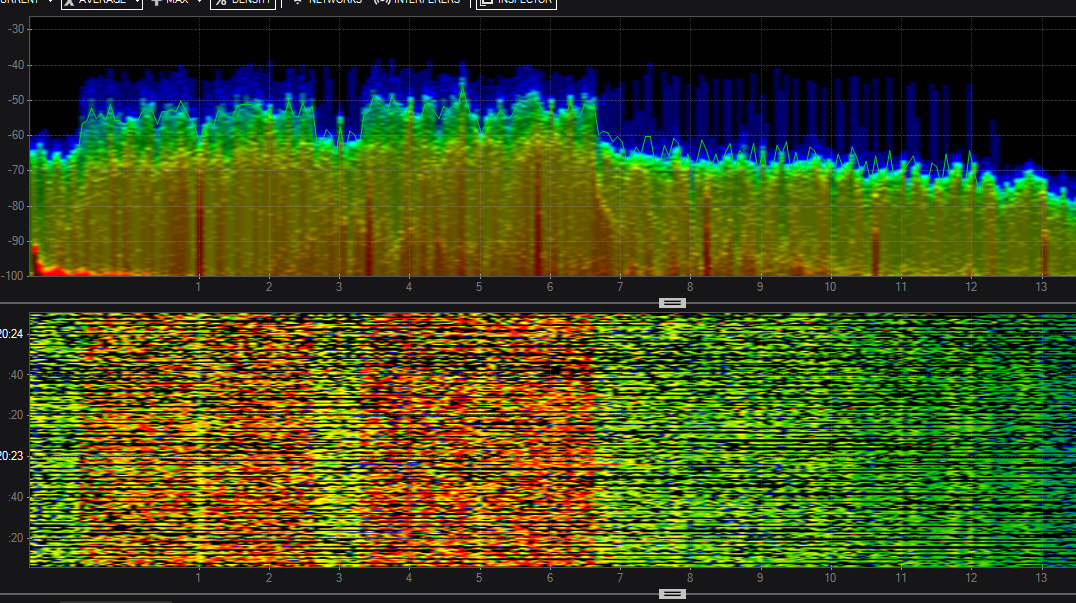
5.0 802.11 n 40 Mhz
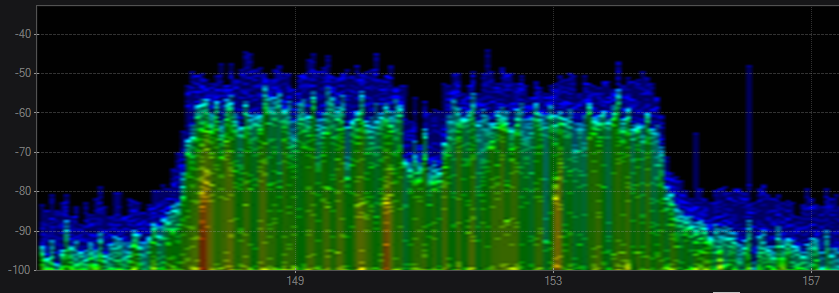
5.0 802.11 ac 80Mhz